Bhuto
Oathkeeper
Nation Name: INDIA
Flag:

Moto: Satya Meva Jayate
Description:
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country (with over 1.2 billion people), and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the south-west, and the Bay of Bengal on the south-east, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north-east; and Myanmar (Burma) and Bangladesh to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; in addition, India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border withThailand and Indonesia. India's capital is New Delhi; other metropolises include Mumbai, Bangalore, Chennai, Hyderabad,Ahmedabad and Kolkata.
Also, India includes Japan also as one of it's state..
Geography:
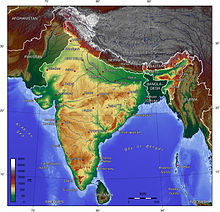
India comprises the bulk of the Indian subcontinent, lying atop the Indian tectonic plate, and part of the Indo-Australian Plate.India's defining geological processes began 75 million years ago when the Indian plate, then part of the southern supercontinent Gondwana, began a north-eastward drift caused by seafloor spreading to its south-west, and later, south and south-east.Simultaneously, the vast Tethyn oceanic crust, to its northeast, began to subduct under the Eurasian plate.These dual processes, driven by convection in the Earth's mantle, both created the Indian Ocean and caused the Indian continental crust eventually to under-thrust Eurasia and to uplift the Himalayas. Immediately south of the emerging Himalayas, plate movement created a vast trough that rapidly filled with river-borne sediment and now constitutes the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Cut off from the plain by the ancient Aravalli Range lies the Thar Desert.
India's coastline measures 7,517 kilometres (4,700 mi) in length; of this distance, 5,423 kilometres (3,400 mi) belong to peninsular India and 2,094 kilometres (1,300 mi) to the Andaman, Nicobar, and Lakshadweep island chains. According to the Indian naval hydrographic charts, the mainland coastline consists of the following: 43% sandy beaches; 11% rocky shores, including cliffs; and 46% mudflats or marshy shores..
Government:
India is a federation with a parliamentary system governed under the Constitution of India, which serves as the country's supreme legal document. It is a republic andrepresentative democracy, in which "majority rule is tempered by minority rights protected by law". Federalism in India defines the power distribution between the federal government and the states. The government abides by constitutional checks and balances. The Constitution of India, which came into effect on 26 January 1950,[172] states in itspreamble that India is a sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic republic.[173] India's form of government, traditionally described as "quasi-federal" with a strong centre and weak states,[174] has grown increasingly federal since the late 1990s as a result of political, economic, and social changes.[175][176]
National symbols[1]
Flag
Tiranga (Tricolour)
Emblem
Sarnath Lion Capital
Language
None[9][10]
Anthem
Jana Gana Mana
Song
Vande Mataram
Currency
₹ (Indian rupee)
Calendar
Flag:

Moto: Satya Meva Jayate
Description:
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country (with over 1.2 billion people), and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the south-west, and the Bay of Bengal on the south-east, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north-east; and Myanmar (Burma) and Bangladesh to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; in addition, India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border withThailand and Indonesia. India's capital is New Delhi; other metropolises include Mumbai, Bangalore, Chennai, Hyderabad,Ahmedabad and Kolkata.
Also, India includes Japan also as one of it's state..
Geography:


India comprises the bulk of the Indian subcontinent, lying atop the Indian tectonic plate, and part of the Indo-Australian Plate.India's defining geological processes began 75 million years ago when the Indian plate, then part of the southern supercontinent Gondwana, began a north-eastward drift caused by seafloor spreading to its south-west, and later, south and south-east.Simultaneously, the vast Tethyn oceanic crust, to its northeast, began to subduct under the Eurasian plate.These dual processes, driven by convection in the Earth's mantle, both created the Indian Ocean and caused the Indian continental crust eventually to under-thrust Eurasia and to uplift the Himalayas. Immediately south of the emerging Himalayas, plate movement created a vast trough that rapidly filled with river-borne sediment and now constitutes the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Cut off from the plain by the ancient Aravalli Range lies the Thar Desert.
India's coastline measures 7,517 kilometres (4,700 mi) in length; of this distance, 5,423 kilometres (3,400 mi) belong to peninsular India and 2,094 kilometres (1,300 mi) to the Andaman, Nicobar, and Lakshadweep island chains. According to the Indian naval hydrographic charts, the mainland coastline consists of the following: 43% sandy beaches; 11% rocky shores, including cliffs; and 46% mudflats or marshy shores..
Government:
India is a federation with a parliamentary system governed under the Constitution of India, which serves as the country's supreme legal document. It is a republic andrepresentative democracy, in which "majority rule is tempered by minority rights protected by law". Federalism in India defines the power distribution between the federal government and the states. The government abides by constitutional checks and balances. The Constitution of India, which came into effect on 26 January 1950,[172] states in itspreamble that India is a sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic republic.[173] India's form of government, traditionally described as "quasi-federal" with a strong centre and weak states,[174] has grown increasingly federal since the late 1990s as a result of political, economic, and social changes.[175][176]
National symbols[1]
Flag
Tiranga (Tricolour)
Emblem
Sarnath Lion Capital
Language
None[9][10]
Anthem
Jana Gana Mana
Song
Vande Mataram
Currency
₹ (Indian rupee)
Calendar
Last edited by a moderator:








